Understanding Basic PLCs: The Foundation of Automation
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential in modern automation, acting as the brain behind efficient and reliable industrial systems. For businesses in the US, automation is not just a trend—it’s a necessity to remain competitive. At Automation Ready Panels, we specialize in delivering tailored automation solutions, including Basic PLC systems, that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
What is a Basic PLC?
A Basic PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a digital computer designed to control industrial processes, machinery, or systems. While advanced PLCs boast complex functionalities, a Basic PLC focuses on essential tasks like:
- Sequential machine operations
- Monitoring inputs and outputs
- Logic-based decision-making
These controllers are ideal for small to mid-sized applications, offering simplicity and reliability at a cost-effective price.
Why Basic PLCs Are Essential
Basic PLCs are fundamental for businesses seeking reliable and cost-effective automation. Here’s why they matter:
1. Cost-Effective Automation
Investing in automation can be daunting for small and medium-sized businesses. Basic PLCs provide a budget-friendly entry point into automation without compromising on quality. With fewer advanced features, they are economical but still meet the demands of many industries.
2. Streamlined Operations
Even in their simplicity, Basic PLCs excel at automating repetitive tasks like turning motors on and off, managing conveyor belts, or controlling lights. This ensures higher efficiency and reduces the margin for human error.
3. Ease of Use
One of the most attractive features of a Basic PLC is its user-friendly interface. With straightforward programming, such as ladder logic, even those with minimal technical knowledge can design and implement automation sequences.
4. Durability and Reliability
Designed to operate in rugged industrial environments, Basic PLCs are built to withstand dust, heat, and vibrations. This durability ensures uninterrupted operation, saving businesses time and maintenance costs.
5. Scalability for Future Growth
While they are labeled “basic,” these PLCs often allow for future upgrades, such as adding more input/output modules or integrating with more advanced systems. This scalability means businesses can grow without starting over.
Common Applications of Basic PLCs
Industries across the US benefit from using Basic PLCs for automation. Common use cases include:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor systems | Streamlined material handling |
| Food & Beverage | Bottling and packaging lines | Consistent quality and speed |
| Agriculture | Irrigation system control | Optimized water usage |
| Energy | Generator management | Enhanced operational reliability |
How Automation Ready Panels Supports Your PLC Needs
At Automation Ready Panels, we understand that every business has unique automation requirements. Here’s how we help:
- Customized Panel Designs: We create control panels that integrate seamlessly with Basic PLCs, tailored to your system’s specifications.
- Turnkey Solutions: From consultation, we handle the entire process to ensure a smooth transition.
- Expert Support: Our team offers ongoing support, including troubleshooting and upgrades.
Benefits of Choosing Automation Ready Panels
- Quality Assurance: Panels designed for durability and compliance with industry standards.
- Fast Turnaround: Timely delivery to keep your project on schedule.
- Local Expertise: Based in the US, we understand the unique needs of American industries.
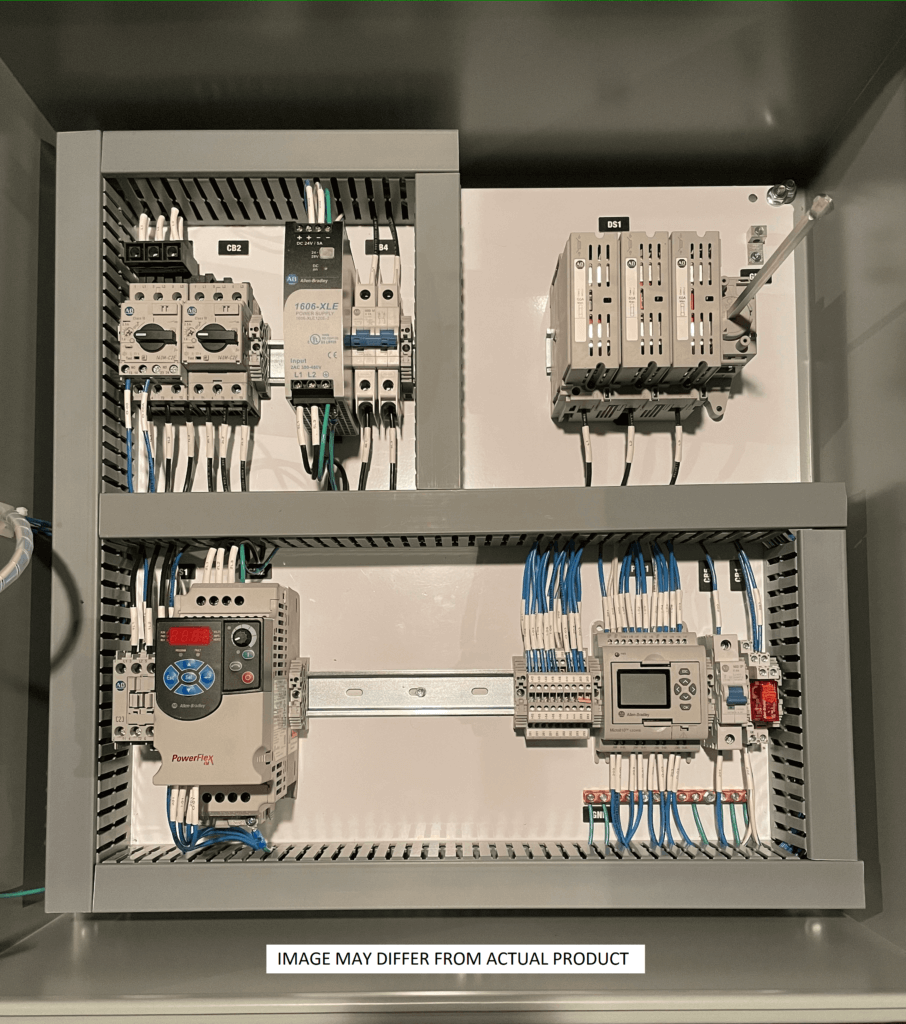
Key Features of a Basic PLC
Basic PLCs have specific features that make them invaluable for small to medium automation tasks.
1. Input/Output (I/O) Modules
The I/O modules are the primary interface between the PLC and the external world.
- Input Modules: Receive signals from devices like sensors, switches, and push buttons, translating them into data the PLC can process.
- Output Modules: Send commands to actuators, such as motors, solenoids, or lights, to perform specific actions.
2. Processor (CPU)
The processor is the brain of the PLC. It executes the programmed logic and processes input data to control outputs. While basic CPUs may not handle complex algorithms, they are optimized for efficiency in simple tasks.
3. Programming Language
Basic PLCs typically use ladder logic programming, which resembles electrical relay diagrams. This visual representation is easy to understand and troubleshoot, even for non-engineers.
4. Communication Ports
Even Basic PLCs offer essential communication options for interacting with other devices. These include:
- USB Ports: For programming and updating.
- Serial Ports (RS-232/RS-485): For device communication, such as connecting to sensors or HMIs (Human Machine Interfaces).
5. Compact Design
Many Basic PLCs come in compact, modular designs that save space and allow easy installation in small control panels.
6. Real-Time Processing
Basic PLCs operate in real-time, meaning they process inputs and trigger outputs almost instantly. This ensures smooth and precise operation in time-sensitive applications.
How to Select the Right Basic PLC for Your Business
Choosing the right PLC can significantly impact the efficiency and scalability of your automation project. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Assess Your Automation Needs
Start by identifying what you need the PLC to do. For example:
- How many devices (sensors, actuators) will it control?
- What type of processes will it automate?
2. Determine the Required I/O Points
Count the number of inputs and outputs your system requires. Basic PLCs are best for smaller systems but can support a range of I/O configurations.
3. Understand Your Environment
Consider the conditions where the PLC will operate. Look for PLCs with appropriate ratings for:
- Temperature Tolerance: If used in hot or cold environments.
- Ingress Protection (IP): For resistance to dust or moisture.
4. Evaluate Communication Needs
If you need the PLC to interact with other systems or devices, ensure it has the necessary communication ports or protocols. For example:
- Do you need USB or Ethernet connectivity?
- Will it need to interface with an HMI or SCADA system?
5. Check Programming Compatibility
Ensure the PLC’s programming language is compatible with your team’s skills. Ladder logic is a popular choice for its simplicity.
6. Consider Future Scalability
While starting with a Basic PLC, think about the potential for expansion. Opt for a modular design if you anticipate adding more I/O points or integrating new systems later.
7. Review Manufacturer Support and Warranty
Choose a brand with a good reputation for reliability and customer support. Many leading manufacturers offer extensive documentation, training resources, and long-term warranties.
8. Budget for Installation and Maintenance
Account for costs beyond the PLC itself, such as wiring, installation, and any necessary maintenance or upgrades.
By considering these factors, you can select a Basic PLC that aligns with your immediate needs while leaving room for future growth.
FAQs About Basic PLCs
What is the lifespan of a Basic PLC?
Basic PLCs typically last 10-20 years, depending on usage and maintenance.
Can I upgrade to an advanced PLC later?
Yes, many Basic PLCs can integrate with advanced models, allowing for scalability.
Do I need professional installation for a Basic PLC?
While Basic PLCs are user-friendly, professional installation ensures optimal performance and safety.
Why Invest in Automation Now?
The global push towards automation has made it a necessity for businesses aiming to reduce costs and improve efficiency. A Basic PLC is an excellent starting point for companies new to automation.
Are you ready to transform your business with Basic PLC solutions? At Automation Ready Panels, we’re committed to helping US businesses harness the power of automation. Contact us today to discuss your needs and get a free consultation!
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$24,073.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$20,321.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$18,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$10,269.00 Select options