NPN vs PNP
NPN vs PNP?
So, what is NPN vs PNP when using a PLC? Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are widely used in industrial control systems to automate processes and control machinery. PLCs use transistors to switch electrical signals, and there are two main types of transistors used in PLCs: NPN and PNP.
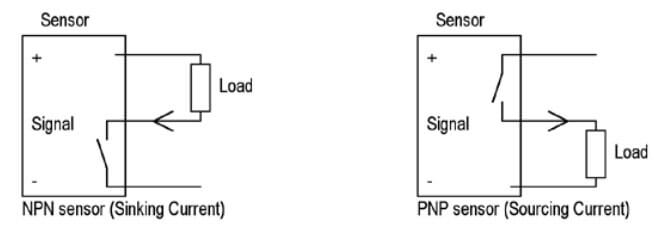
NPN transistors, also known as negative-positive-negative transistors, are the most commonly used type in PLCs. They work by using a small current applied to the base terminal to control a larger current flowing through the collector and emitter terminals. This type of transistor is known for its ability to switch quickly and handle high current loads.
PNP transistors, on the other hand, are positive-negative-positive transistors. They work in the opposite way of NPN transistors, with a small current applied to the base terminal controlling the flow of a larger current through the collector and emitter terminals. PNP transistors are less commonly used in PLCs, but they have the advantage of being able to handle high voltage loads and provide a higher level of isolation between the input and output terminals.
The main difference between NPN vs PNP transistors is their polarity. NPN transistors are N-type semiconductors, while PNP transistors are P-type semiconductors. This means that NPN transistors have a negative terminal and a positive terminal, while PNP transistors have a positive terminal and a negative terminal. As a result, NPN vs PNP transistors have opposite polarities and therefore work in opposite ways.
In summary, NPN and PNP transistors are the two main types of transistors used in PLCs. NPN transistors are more commonly used, and are known for their ability to switch quickly and handle high current loads. PNP transistors, on the other hand, are less commonly used but have the advantage of being able to handle high voltage loads and provide a higher level of isolation between the input and output terminals. The main difference between the two is their polarity, with NPN transistors having a negative terminal and a positive terminal, while PNP transistors have a positive terminal and a negative terminal.
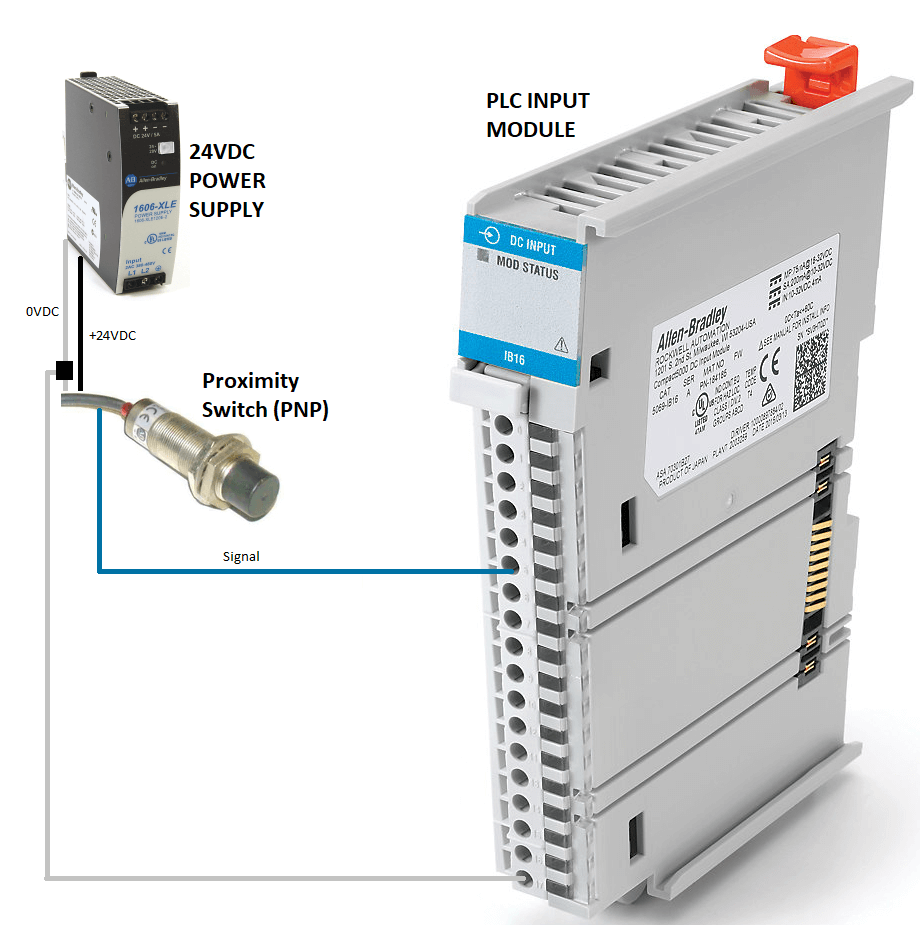
CompactLogix input modules can use both NPN and PNP transistors. The specific type of transistor used will depend on the specific input module being used and the type of sensor or device that it is connecting to.
For example, the Allen-Bradley 1769-IF8 CompactLogix Input Module supports both NPN and PNP transistor-transistor logic (TTL) inputs, as well as sourcing and sinking inputs. This means that it can connect to both NPN and PNP devices and sensors and can detect both high and low voltage levels.
It’s important to note that the type of input module and the type of sensor or device that it is connecting to, will determine the type of transistor used. Before installing the module, check the specifications of the module and ensure that it is compatible with the device or sensor you will be connecting to it.
Wanting to dig deeper into NPN vs PNP? Need to bounce your questions off an expert? Contact Us
SHOP NOW
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$24,073.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$20,321.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$18,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$10,269.00 Select options