The Rise of Automation for Chemical Manufacturers
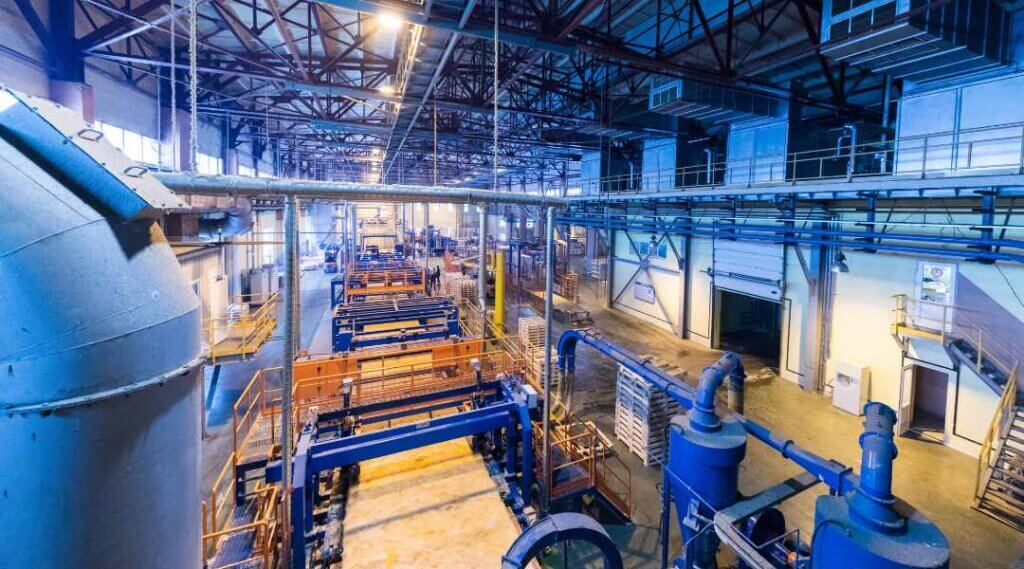
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, chemical manufacturers are increasingly turning to automation to stay competitive, enhance safety, and boost productivity. This technological revolution is reshaping the industry, offering unprecedented opportunities for growth and efficiency. Let’s dive deep into the world of automation in chemical manufacturing and explore how it’s transforming the sector.
What is Automation in the Chemical Industry for Chemical Manufacturers?
Automation in the chemical industry involves using technology to control and monitor chemical processes with minimal human intervention. It’s not just about robots and machines; it’s a holistic approach to optimizing every aspect of chemical production.
The chemical sector employs various types of automation:
- Process control systems that manage complex chemical reactions
- Robotic systems for material handling and packaging
- Advanced data analytics for quality control and predictive maintenance
Key players like Rockwell Automation, Siemens, and ABB are at the forefront, developing cutting-edge solutions tailored for chemical manufacturers. These industry giants are constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in industrial automation.
The Benefits of Automation for Chemical Manufacturers
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Automation is a game-changer when it comes to boosting efficiency in chemical plants. By streamlining processes and reducing manual labor, manufacturers can achieve remarkable productivity gains.
For instance, automated systems can:
- Optimize production schedules based on real-time demand
- Ensure precise control of chemical reactions, reducing variability
- Coordinate complex multi-step processes with pinpoint accuracy
The result? Higher output, consistent quality, and the ability to respond quickly to market demands.
Improved Safety and Risk Management
Safety is paramount in the chemical industry, and automation plays a crucial role in protecting workers and the environment.
Key safety benefits include:
- Minimizing human exposure to hazardous chemicals through remote operation
- Implementing robust Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) to prevent accidents
- Continuous monitoring of critical parameters like temperature and pressure
By taking humans out of harm’s way and providing constant vigilance, automation significantly reduces the risk of accidents and environmental incidents.
Cost Reduction and Profitability
While the initial investment in automation can be substantial, the long-term financial benefits are undeniable. Automated systems help chemical manufacturers:
- Lower operating costs by reducing labor requirements
- Minimize waste through precise control of raw materials
- Optimize energy consumption, a major expense in chemical production
- Increase throughput and yield, maximizing the value of each production run
These cost savings translate directly to improved profitability, giving automated plants a competitive edge in the market.
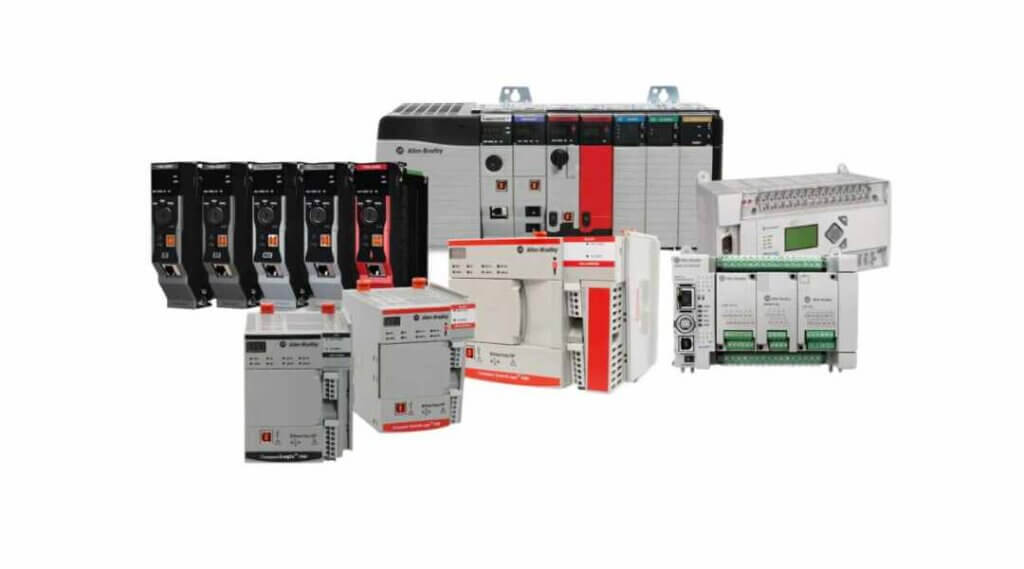
Key Automation Technologies in Chemical Manufacturing
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs are the workhorses of industrial automation. In chemical manufacturing, they:
- Control individual processes and equipment
- Execute predefined sequences and safety interlocks
- Provide real-time data to higher-level control systems
Their reliability and flexibility make PLCs indispensable in modern chemical plants.
Distributed Control Systems (DCS)
For managing complex plant-wide operations, Distributed Control Systems are the go-to solution. DCS platforms:
- Integrate control of multiple processes and units
- Provide centralized monitoring and operation
- Offer advanced control strategies for process optimization
DCS technology allows operators to manage entire chemical plants from a single control room, improving efficiency and safety.
SCADA Systems
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems provide a bird’s-eye view of plant operations. They excel at:
- Collecting data from diverse sources across the plant
- Visualizing process information for operators
- Enabling remote monitoring and control
SCADA systems are particularly valuable for chemical companies with multiple sites or geographically dispersed operations.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The IIoT is revolutionizing how chemical plants collect and use data. Key components include:
Smart Transducers and Actuators
These intelligent devices:
- Measure process variables with high accuracy
- Communicate data in real-time to control systems
- Can be remotely configured and diagnosed
Smart instruments provide the foundation for data-driven decision-making in chemical manufacturing.
Robotics and Material Handling
Robotic systems are increasingly common in chemical plants, where they:
- Automate repetitive tasks like packaging and palletizing
- Improve material flow and inventory management
- Enhance worker safety by handling hazardous materials
From articulated robots to autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs), these systems are transforming plant logistics.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Automation for Chemical Manufacturers
Initial Investment Costs
The upfront cost of automation can be daunting for some chemical manufacturers. However, savvy companies are finding ways to mitigate these costs:
- Phased implementation approaches
- Leveraging vendor financing options
- Focusing on high-ROI applications first
By carefully planning their automation strategy, manufacturers can balance costs with benefits.
Technical Expertise and Training
Automation requires a skilled workforce to design, implement, and maintain systems. Chemical companies are addressing this challenge by:
- Investing in training programs for existing staff
- Partnering with automation vendors for knowledge transfer
- Recruiting automation specialists from other industries
Building in-house expertise is crucial for long-term success with automation technologies.
Cybersecurity Risks
As chemical plants become more connected, they also become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Robust security measures are essential, including:
- Network segmentation and firewalls
- Regular security audits and penetration testing
- Employee training on cybersecurity best practices
Protecting automated systems from cyber attacks is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance.
The Future of Automation in Chemical Manufacturing for Chemical Manufacturers
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are set to take chemical automation to new heights. Future applications include:
- Predictive maintenance to prevent equipment failures
- Real-time process optimization based on market conditions
- Autonomous plant operation with minimal human intervention
As these technologies mature, they promise to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency and agility in chemical manufacturing.
Digital Twins and Simulation
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical plants, enabling:
- Risk-free testing of process changes
- Operator training in a safe, simulated environment
- Optimization of plant design before construction
This powerful tool is becoming indispensable for chemical companies looking to innovate and improve their operations.
The Role of Big Data and Analytics
The chemical industry generates vast amounts of data. Advanced analytics will help companies:
- Identify patterns and trends across complex processes
- Optimize supply chains and logistics
- Drive continuous improvement in quality and efficiency
As data analysis techniques evolve, chemical manufacturers will gain ever-deeper insights into their operations.
Conclusion
Automation is not just a trend in chemical manufacturing—it’s a fundamental shift that’s reshaping the industry. That is the future of chemical manufacturing. From improved safety and efficiency to cost reduction and enhanced quality, the benefits are clear and compelling.
As we’ve seen, successful automation requires careful planning, investment in technology and people, and a commitment to ongoing improvement. The challenges are real, but so are the rewards for companies that get it right.
For chemical manufacturers looking to stay competitive in an increasingly complex global market, embracing automation is not just an option—it’s a necessity. The future belongs to those who can harness the power of technology to drive innovation and excellence in chemical production.
Ready to take your chemical manufacturing operations to the next level with automation? Look no further than Automation Ready Panels. Our tailored solutions are designed to meet the unique challenges of the chemical industry, providing you with the tools and expertise you need to optimize your processes, enhance safety, and boost your bottom line. Don’t let your competitors get ahead—contact Automation Ready Panels today and discover how we can help you build a smarter, more efficient chemical manufacturing operation for the future.
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$24,073.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$20,321.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$18,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$10,269.00 Select options