SCADA in the Chemical Industry: A Comprehensive Overview
In today’s fast-paced chemical industry, staying ahead of the curve isn’t just about innovation—it’s about mastering the delicate balance between safety, efficiency, and compliance. Enter SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), the unsung hero revolutionizing how chemical plants operate.
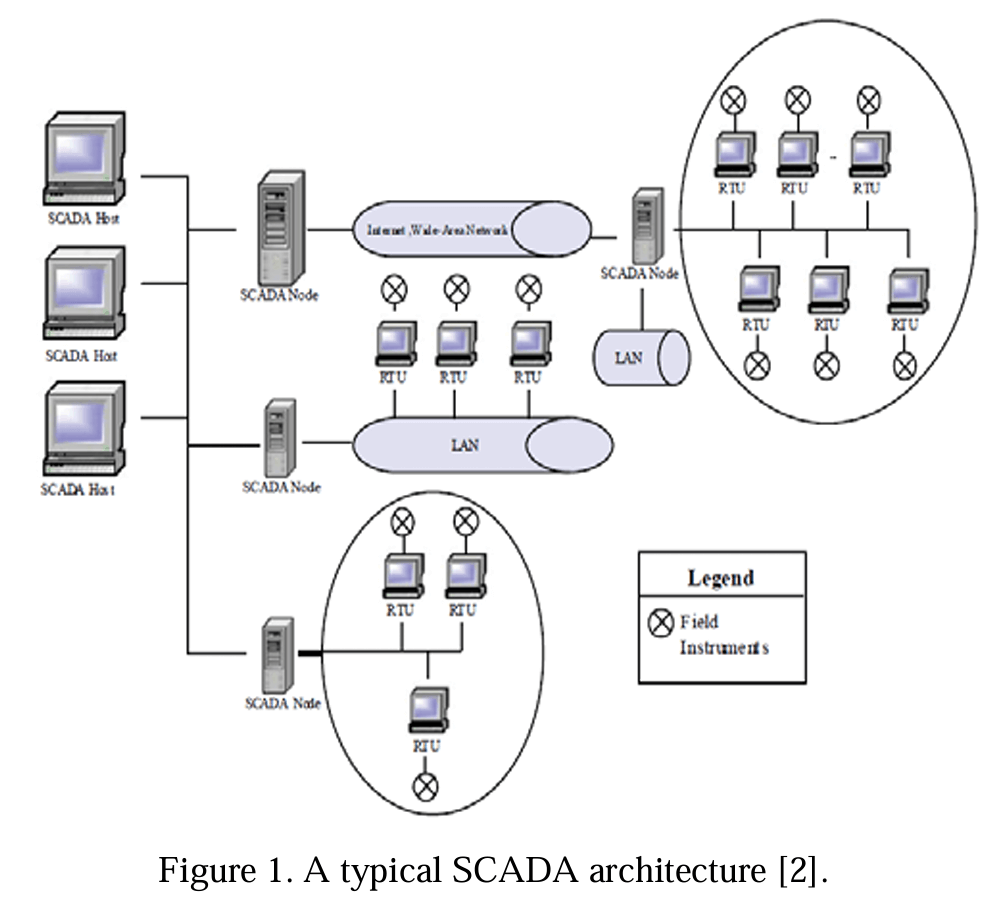
Picture this: a bustling chemical facility where every process, every reaction, and every safety protocol is monitored and controlled with pinpoint accuracy. That’s the power of SCADA in action. But what makes it so crucial? How does it transform the landscape of chemical manufacturing? And most importantly, how can you harness its potential to skyrocket your plant’s performance?
In this deep dive, we’ll unravel the complexities of SCADA systems in the chemical industry. We’ll explore how they’re not just improving safety protocols but redefining them. We’ll get into the nitty-gritty of how SCADA boosts productivity, sometimes in ways you might not expect. And we’ll take a close look at cutting-edge solutions like FactoryTalk View Studio and FactoryTalk Optix, tools that are changing the game for modern SCADA implementations.
Here’s what you’ll discover:
- How SCADA systems are revolutionizing safety measures in chemical plants, making split-second decisions that could save lives.
- The surprising ways SCADA is boosting efficiency, from optimizing processes to predicting maintenance needs before problems arise.
- Why the future of chemical manufacturing hinges on mastering SCADA technology, and how you can stay ahead of the curve.
So, buckle up. Whether you’re a seasoned chemical engineer, a plant manager looking to upgrade your systems, or just curious about the tech shaping our industrial future, this guide is your roadmap to understanding SCADA in the chemical industry. Let’s dive in and uncover how this powerful technology is transforming chemical plants into safer, more efficient, and incredibly sophisticated operations.
SCADA’s Impact on Safety and Risk Mitigation in Chemical Plants
In the high-stakes world of chemical manufacturing, safety isn’t just a priority—it’s the cornerstone of every operation. SCADA systems have emerged as the vigilant guardians of chemical plants, dramatically reshaping safety protocols and risk management strategies.
At its core, SCADA acts as the nervous system of a chemical plant. It collects data from a myriad of sensors spread throughout the facility, monitoring critical parameters like temperature, pressure, flow rates, and chemical compositions in real-time. But SCADA doesn’t just passively observe; it actively interprets this data, making split-second decisions that can prevent disasters before they happen.
Let’s break down how SCADA elevates safety in chemical plants:
- Real-time Monitoring and Control:
- Continuous surveillance of critical processes
- Instant detection of anomalies or deviations from safe operating ranges
- Automated adjustments to maintain optimal conditions
- Alarm Management:
- Sophisticated alarm hierarchies that prioritize critical alerts
- Customizable thresholds to prevent alarm fatigue
- Integration with notification systems for rapid response
- Emergency Response Coordination:
- Automated shutdown procedures for extreme situations
- Coordination of safety systems (e.g., fire suppression, ventilation)
- Guided operator response protocols
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Automated logging of process data for compliance reporting
- Real-time monitoring of emissions and effluents
- Facilitation of audit trails and incident investigations
Importance of SCADA in Chemical Plants
Consider a scenario where a reactor’s temperature begins to rise unexpectedly. A SCADA system can detect this change instantly, alert operators, and even initiate cooling procedures automatically if the situation becomes critical. This level of responsiveness can mean the difference between a minor hiccup and a catastrophic event.
Moreover, SCADA systems play a crucial role in risk mitigation beyond immediate safety concerns. By providing comprehensive data on plant operations, these systems enable predictive maintenance strategies. This proactive approach helps identify potential equipment failures or process inefficiencies before they escalate into safety hazards.
SCADA’s impact on regulatory compliance cannot be overstated. In an industry where adherence to environmental and safety regulations is paramount, SCADA systems provide the detailed, accurate record-keeping required by regulatory bodies. From emissions monitoring to process validation, SCADA ensures that chemical plants can demonstrate their compliance with confidence.
The integration of SCADA with other safety systems further enhances its effectiveness. For instance, linking SCADA with gas detection systems allows for immediate response to leaks, including automated ventilation and evacuation alerts. Similarly, integration with fire detection and suppression systems enables a coordinated, rapid response to fire hazards.
By providing a clear, real-time picture of plant operations, SCADA empowers operators and managers to make informed decisions quickly. This enhanced situational awareness is invaluable in high-pressure situations where every second counts.
In essence, SCADA has transformed safety in the chemical industry from a reactive approach to a proactive, predictive model. It’s not just about responding to incidents anymore; it’s about preventing them before they occur. As we continue to push the boundaries of chemical manufacturing, the role of SCADA in ensuring safe operations will only grow more critical.
Boosting Efficiency and Productivity with SCADA
While safety is paramount in chemical plants, efficiency and productivity are the engines that drive profitability and innovation. SCADA systems, once primarily viewed as safety tools, have evolved into powerful catalysts for operational excellence. Let’s explore how SCADA is revolutionizing efficiency and productivity in the chemical industry.
Process Optimization
SCADA systems are the maestros of chemical processes, conducting a complex symphony of reactions and operations with precision. By continuously monitoring and adjusting process parameters, SCADA ensures that each operation runs at its optimal point. This might mean:
-
- Fine-tuning reactor temperatures to maximize yield
- Adjusting flow rates to optimize mixing and reaction times
- Balancing feedstock ratios for ideal product composition
- The result? Higher quality products, reduced waste, and more consistent output.
Downtime Reduction
Unplanned downtime is the nemesis of productivity in chemical plants. SCADA tackles this challenge head-on:
-
- Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze equipment performance data to forecast potential failures
- Condition-based monitoring triggers maintenance activities only when needed, reducing unnecessary downtime
- Rapid fault diagnosis and guided troubleshooting accelerate recovery times
- By minimizing downtime, SCADA keeps production lines humming and profits flowing.
Energy Efficiency
In energy-intensive chemical processes, even small improvements in efficiency can lead to significant cost savings. SCADA systems optimize energy use by:
-
- Dynamically adjusting equipment operation based on demand
- Identifying and eliminating energy waste in processes
- Facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into plant operations
Resource Management
SCADA’s data collection capabilities extend beyond process control to encompass resource management:
-
- Real-time inventory tracking of raw materials and finished products
- Optimized scheduling of batch processes to maximize equipment utilization
- Improved supply chain coordination through integration with ERP systems
Data-Driven Continuous Improvement
Perhaps SCADA’s most transformative impact on efficiency comes from its role in continuous improvement initiatives:
-
- Historical data analysis reveals trends and opportunities for process refinement
- What-if simulations allow engineers to test process modifications virtually before implementation
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI) tracking provides clear metrics for measuring and improving efficiency
Integration with Other Systems
SCADA doesn’t operate in isolation. Its true power is unleashed when integrated with other enterprise systems:
-
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for seamless order processing and production planning
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for detailed production tracking and quality control
- Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) for real-time quality assurance
- This integration creates a holistic view of operations, enabling data-driven decision-making at all levels of the organization.
Human Efficiency
While we often focus on process efficiency, SCADA also dramatically improves human efficiency:
-
- Intuitive HMI designs reduce operator cognitive load and improve response times
- Mobile access allows managers to monitor plant performance remotely
- Automated reporting frees up staff time for more value-added activities
By harnessing the power of SCADA, chemical plants are not just becoming more efficient—they’re becoming smarter. The system’s ability to collect, analyze, and act on vast amounts of data in real-time is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in chemical manufacturing.
As we look to the future, the role of SCADA in driving efficiency and productivity will only grow. With the integration of advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI, these systems will become even more adept at optimizing operations, predicting issues, and uncovering new opportunities for improvement.
In the next section, we’ll explore two powerful SCADA solutions that are at the forefront of this revolution: FactoryTalk View Studio and FactoryTalk Optix. These tools are empowering chemical manufacturers to take their operations to new heights of efficiency and productivity.
FactoryTalk View Studio and FactoryTalk Optix: Modern SCADA Software Solutions
As the chemical industry evolves, so too must the tools we use to monitor and control our processes. Enter FactoryTalk View Studio and FactoryTalk Optix—two cutting-edge SCADA software solutions that are reshaping how chemical plants operate. Let’s dive into these powerful platforms and explore how they’re pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in modern SCADA implementations.
FactoryTalk View Studio: The Powerhouse of HMI/SCADA Development
FactoryTalk View Studio stands out as a robust, versatile platform for creating sophisticated Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) and SCADA applications. Here’s why it’s becoming a go-to solution for many chemical plants:
- Intuitive Design Environment:
- Drag-and-drop functionality for rapid interface creation
- Extensive library of pre-built objects and animations
- Support for custom graphics and animations
- Scalability:
- Suitable for both small, single-user applications and large, distributed systems
- Easy expansion as plant needs grow
- Seamless Integration:
- Direct connectivity with Rockwell Automation’s PLCs and other industrial control systems
- OPC support for third-party device integration
- Advanced Alarming and Trending:
- Sophisticated alarm management with prioritization and filtering
- Real-time and historical trending for in-depth process analysis
- Scripting Capabilities:
- VBA scripting for custom functionality and complex logic
- Ability to create reusable code modules for efficiency
- Multi-language Support:
- Easy switching between languages for global operations
- Unicode support for non-Latin character sets
- Security Features:
- Role-based access control
- Audit trail functionality for regulatory compliance
FactoryTalk View Studio shines in chemical plants where complex processes require equally sophisticated monitoring and control interfaces. Its ability to create rich, interactive displays allows operators to quickly grasp process states and take appropriate action. The platform’s trending and analysis tools are particularly valuable for optimizing chemical reactions and identifying opportunities for process improvement.
FactoryTalk Optix: The Next Generation of Cloud-Enabled SCADA
While FactoryTalk View Studio excels in traditional SCADA applications, FactoryTalk Optix represents the future of SCADA technology. This cloud-native platform brings a host of new capabilities to the table:
- Cloud-First Architecture:
- Built from the ground up for cloud deployment
- Seamless scalability and redundancy
- Reduced on-premise IT infrastructure requirements
- Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Runs on Windows, Linux, and cloud platforms
- Web-based interfaces accessible from any device with a browser
- Open and Extensible:
- Based on .NET Core for easy customization and extension
- Support for custom modules and third-party integrations
- Advanced Visualization:
- Support for 3D graphics and augmented reality (AR) interfaces
- Dynamic, data-driven visualizations
- Edge Computing Capabilities:
- Distributed intelligence for reduced latency and improved reliability
- Local data processing to minimize cloud data transfer
- IoT Integration:
- Native support for IoT protocols like MQTT
- Easy integration with cloud-based analytics and AI services
- Collaborative Development:
- Multi-user development environment
- Version control and project management tools built-in
FactoryTalk Optix and IIoT
FactoryTalk Optix is particularly well-suited for chemical plants looking to leverage the latest in IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) and Industry 4.0 technologies. Its cloud-native architecture enables new levels of data integration and analysis, while its advanced visualization capabilities can create immersive, information-rich operator environments.
Imagine a chemical plant where operators can use AR headsets to “see” inside reactors, with real-time data overlays showing temperatures, pressures, and chemical compositions. Or consider a facility where AI-powered analytics, running on the cloud, continuously optimize processes based on market demand, energy prices, and equipment health. These scenarios, once the stuff of science fiction, are becoming reality with platforms like FactoryTalk Optix.
Both FactoryTalk View Studio and FactoryTalk Optix offer powerful solutions for modern SCADA implementations in the chemical industry. While View Studio provides a robust, proven platform for traditional SCADA applications, Optix opens up new possibilities with its cloud-native, IoT-ready architecture.
The choice between these platforms will depend on your specific needs, existing infrastructure, and future goals. Many chemical plants are finding success with a hybrid approach, using View Studio for critical, on-premise systems while leveraging Optix for newer, cloud-enabled applications.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in chemical manufacturing, platforms like FactoryTalk View Studio and FactoryTalk Optix will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring our operations are safe, efficient, and ready for the challenges of tomorrow.
Addressing Security and Cyberattack Risks in SCADA Systems
In an era where digital transformation is reshaping the chemical industry, the security of SCADA systems has become a critical concern. These systems, once isolated from external networks, are now increasingly connected to the internet and corporate IT systems, exposing them to a wide range of cybersecurity threats. Let’s explore the unique challenges faced by SCADA systems in the chemical industry and strategies to mitigate these risks.
Unique Security Challenges in Chemical Industry SCADA Systems
- Legacy Systems: Many chemical plants still rely on older SCADA systems that were not designed with modern cybersecurity threats in mind. These legacy systems often lack basic security features and can be challenging to update or patch.
- 24/7 Operation Requirements: The continuous nature of many chemical processes makes it difficult to take systems offline for updates or security maintenance. This can lead to delayed patching and persistent vulnerabilities.
- Complex Integration: SCADA systems in chemical plants often need to integrate with a wide range of other systems (ERP, MES, LIMS, etc.), increasing the attack surface and potential entry points for malicious actors.
- Physical Safety Implications: Unlike many IT systems, a compromise of SCADA systems in a chemical plant could have severe real-world consequences, potentially leading to environmental disasters or loss of life.
- Regulatory Compliance: Chemical plants must navigate a complex landscape of safety and environmental regulations, adding another layer of complexity to security efforts.
Potential Cyberattack Vectors and Their Impact
- Network-Based Attacks:
- Man-in-the-middle attacks to intercept and manipulate control signals
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks to disrupt operations
- Exploitation of unsecured remote access points
- Malware and Ransomware:
- Specialized industrial control system (ICS) malware like Triton or Industroyer
- Ransomware attacks that could lock operators out of critical systems
- Social Engineering:
- Phishing attacks targeting plant personnel with access to SCADA systems
- Insider threats from disgruntled employees or contractors
- Supply Chain Attacks:
- Compromised software updates or hardware components
- Vulnerabilities in third-party systems integrated with SCADA
The impact of these attacks could range from production disruptions and financial losses to catastrophic safety incidents or environmental damage. In 2017, a petrochemical plant in Saudi Arabia was targeted by the Triton malware, which attempted to disable safety systems. While this attack was fortunately thwarted, it highlighted the potential for devastating consequences if SCADA systems are compromised.
Best Practices for Securing SCADA Systems
- Network Segmentation:
- Implement a demilitarized zone (DMZ) between the SCADA network and corporate IT systems
- Use firewalls and virtual LANs (VLANs) to isolate critical control systems
- Employ unidirectional gateways where possible to prevent unauthorized data flow
- Access Control:
- Implement strong authentication mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication for remote access
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to limit user privileges
- Regularly audit and update access rights, especially for third-party vendors and contractors
- Patch Management:
- Develop a comprehensive patch management strategy that balances security needs with operational constraints
- Use virtual patching or compensating controls when immediate patching isn’t feasible
- Regularly test patches in a non-production environment before deployment
- Encryption:
- Encrypt all data in transit, especially for remote access connections
- Consider encrypting sensitive data at rest, such as configuration files and historical data
- Continuous Monitoring and Logging:
- Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) tailored for industrial control system environments
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to correlate and analyze security events
- Maintain comprehensive logs and conduct regular security audits
- Employee Training and Awareness:
- Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training for all personnel with SCADA access
- Develop and enforce clear policies for secure SCADA operation and maintenance
- Create a culture of security awareness throughout the organization
- Incident Response Planning:
- Develop and regularly test an incident response plan specific to SCADA systems
- Establish clear communication channels and roles for responding to security incidents
- Conduct tabletop exercises to simulate various attack scenarios
- Vendor Management:
- Carefully vet third-party vendors and contractors with access to SCADA systems
- Include security requirements in contracts and service level agreements (SLAs)
- Regularly assess and audit vendor security practices
Emerging Technologies in SCADA Security
The landscape of SCADA security is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to combat sophisticated threats:
- AI and Machine Learning:
- Anomaly detection algorithms to identify unusual system behavior
- Predictive analytics to forecast potential security incidents
- Automated threat hunting and response
- Blockchain:
- Immutable logging of SCADA transactions and configuration changes
- Secure, decentralized authentication mechanisms
- Zero Trust Architecture:
- Assuming no user or device is trustworthy by default
- Continuous verification and least privilege access
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) Security:
- Specialized security solutions for IoT devices integrated with SCADA systems
- Edge computing for local security processing and reduced attack surface
As SCADA systems in the chemical industry become more connected and sophisticated, so too must our approach to securing them. It’s no longer enough to rely on air gaps or perimeter defenses. Instead, we need a holistic, layered approach to security that encompasses technology, processes, and people.
Remember, security is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Regular risk assessments, security audits, and continuous improvement are essential to staying ahead of evolving threats. By implementing these best practices and leveraging emerging technologies, chemical plants can significantly enhance the security of their SCADA systems, ensuring safe and reliable operations in an increasingly digital world.
The Future of SCADA in the Chemical Industry
As we stand on the cusp of a new industrial revolution, the future of SCADA in the chemical industry looks both exciting and transformative. Emerging technologies are set to reshape how we monitor, control, and optimize chemical processes, pushing the boundaries of efficiency, safety, and innovation. Let’s explore the trends that are shaping the future of SCADA and their potential impact on the chemical industry.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The proliferation of IoT devices is set to revolutionize SCADA systems:
- Ubiquitous Sensing: Miniaturized, low-power sensors will enable more comprehensive and granular monitoring of chemical processes.
- Edge Computing: Distributed intelligence at the edge will allow for faster response times and reduced data transmission loads.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT-enabled equipment will provide real-time health data, enabling truly predictive maintenance strategies.
Imagine a chemical plant where every valve, pump, and reactor is equipped with smart sensors, continuously streaming data to the SCADA system. This level of visibility will enable unprecedented optimization and control.
2. Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics
The cloud is set to play a pivotal role in the future of SCADA:
- Scalable Processing: Cloud platforms will provide the computational power needed to analyze vast amounts of process data in real-time.
- Advanced Analytics: Machine learning and AI algorithms running in the cloud will uncover insights and optimization opportunities that were previously invisible.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud-based SCADA will enable seamless monitoring and control of distributed chemical facilities from anywhere in the world.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are poised to transform SCADA from a monitoring and control system to an intelligent decision-making platform:
- Autonomous Operation: AI-powered SCADA systems will be capable of making complex decisions and adjustments without human intervention.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models will forecast equipment failures, process deviations, and even market demand with increasing accuracy.
- Natural Language Processing: Operators will be able to interact with SCADA systems using voice commands and natural language queries.
4. Augmented and Virtual Reality
AR and VR technologies will revolutionize how operators interact with SCADA systems:
- Immersive Visualization: VR environments will allow operators to “walk through” digital twins of chemical plants, inspecting equipment and processes in unprecedented detail.
- AR-Enhanced Operations: Operators wearing AR glasses will see real-time process data overlaid on physical equipment, enabling intuitive decision-making.
- Remote Collaboration: AR/VR technologies will facilitate remote expert assistance, allowing specialists to guide on-site personnel through complex procedures.
5. Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Blockchain has the potential to enhance the security and traceability of SCADA systems:
- Immutable Audit Trails: Blockchain can provide tamper-proof logs of all SCADA transactions and configuration changes.
- Supply Chain Integration: Blockchain-enabled SCADA systems could seamlessly track raw materials from source to finished product, enhancing quality control and regulatory compliance.
- Smart Contracts: Automated, blockchain-based contracts could govern complex multi-party chemical processes, ensuring transparency and trust.
6. 5G and Advanced Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks will enable new possibilities for SCADA systems:
- Ultra-Low Latency: 5G’s near-instantaneous communication will allow for real-time control of even the most time-sensitive chemical processes.
- Massive Device Connectivity: 5G networks will support a vastly increased number of connected devices, enabling truly comprehensive IoT integration.
- Network Slicing: 5G’s ability to create virtual, isolated network slices will enhance security and reliability for critical SCADA functions.
7. Human-Centric Design and Operator Empowerment
As SCADA systems become more advanced, there will be an increased focus on human-centric design:
- Intuitive Interfaces: Next-generation HMIs will adapt to individual operator preferences and cognitive styles.
- Skill Augmentation: SCADA systems will act as intelligent assistants, enhancing operator decision-making rather than replacing human judgment.
- Continuous Learning: Integrated e-learning modules will keep operators up-to-date with the latest process improvements and safety protocols.
The Growing Importance of Skilled Professionals
As SCADA systems in the chemical industry become more sophisticated, the demand for skilled professionals will only increase:
- Interdisciplinary Expertise: Future SCADA engineers will need a blend of chemical engineering knowledge, IT skills, and cybersecurity expertise.
- Continuous Learning: Professionals will need to commit to lifelong learning to keep pace with rapidly evolving technologies.
- Ethical Considerations: As AI plays a larger role in decision-making, engineers will need to grapple with complex ethical questions surrounding autonomy and responsibility.
Conclusion
The future of SCADA in the chemical industry is one of unprecedented connectivity, intelligence, and integration. These systems will evolve from passive monitoring tools to active partners in process optimization and decision-making. They will break down silos between operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT), creating a seamless digital ecosystem that spans from the reactor to the boardroom.
However, with great power comes great responsibility. As SCADA systems become more connected and autonomous, issues of cybersecurity, data privacy, and ethical AI use will come to the forefront. Chemical companies will need to navigate these challenges carefully, balancing the benefits of advanced SCADA technologies with the need for safety, security, and regulatory compliance.
The chemical plants of tomorrow will be smarter, more efficient, and more responsive than ever before, thanks to the evolution of SCADA systems. But realizing this future will require more than just technology—it will demand a workforce of skilled, adaptable professionals who can bridge the worlds of chemistry, computing, and control systems.
For those in the chemical industry, the message is clear: the future of SCADA is bright, but it requires proactive engagement. Investing in the right technologies, developing the necessary skills, and fostering a culture of innovation will be key to thriving in this new era of intelligent, connected chemical manufacturing.
Contact Automation Ready Panels Today
As we look to this exciting future, it’s crucial to have the right partners and tools to navigate the complexities of modern SCADA implementations. This is where Automation Ready Panels comes in. With their expertise in cutting-edge automation solutions, including advanced SCADA systems, they are ideally positioned to help chemical companies make the leap into the future of process control and optimization.
Whether you’re looking to upgrade your existing SCADA system, implement new IoT-enabled sensors, or develop a comprehensive digital transformation strategy, Automation Ready Panels has the knowledge and experience to guide you every step of the way. Their team of experts can help you leverage the latest technologies while ensuring your systems remain secure, compliant, and optimized for your specific needs.
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$24,073.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$20,321.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$18,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$10,269.00 Select options