Future of Automation in Chemical Manufacturing: A Paradigm Shift
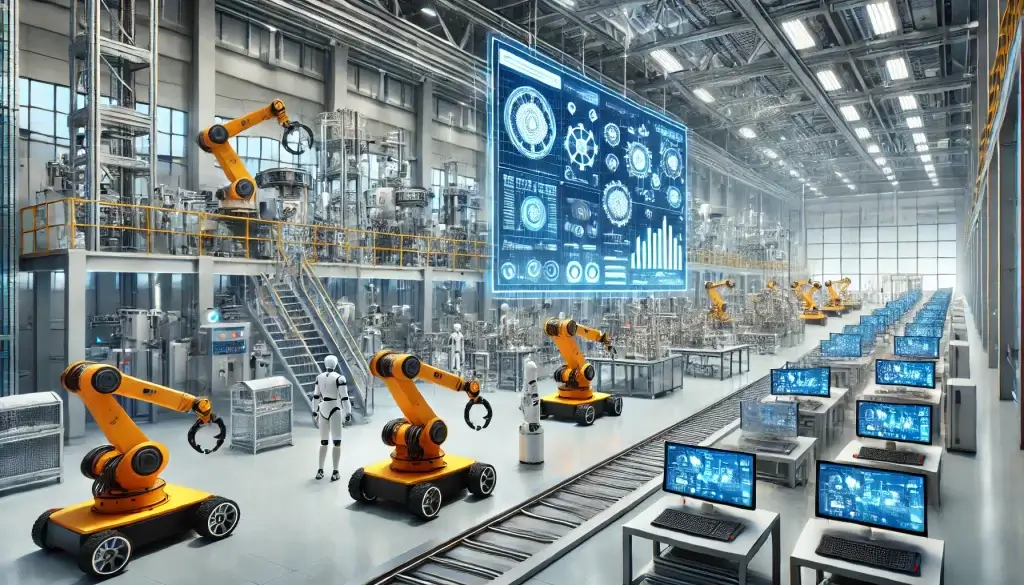
The chemical industry is poised for a revolutionary transformation. As we plunge headfirst into Industry 4.0, automation is reshaping the landscape of chemical manufacturing. This shift promises to usher in a new age of efficiency, safety, and sustainability, fundamentally altering how we produce the chemicals that power our world.
Gone are the days of manual processes and isolated systems. Today’s chemical plants are evolving into smart, interconnected hubs of innovation. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge technologies, manufacturers are unlocking unprecedented levels of productivity and precision.
But what exactly does this automated future look like? And how can chemical companies prepare for this seismic shift? Let’s explore the technologies, benefits, and challenges that define the automated chemical plant of tomorrow.
Key Technologies Driving Automation in Chemical Plants
Advanced technologies are fueling the automation revolution in chemical manufacturing. Each plays a crucial role in creating the smart, efficient plants of the future.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are the brains behind the automated chemical plant. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and make real-time decisions.
In quality control, AI-powered systems can detect minute deviations in product composition, ensuring consistent output. ML algorithms can suggest ideal conditions for maximum yield for chemical reaction optimization, often discovering novel approaches human experts might overlook.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Smart Sensors
The IIoT forms the nervous system of the automated plant. Smart sensors distributed throughout the facility collect real-time data on everything from temperature and pressure to chemical composition.
This constant stream of information allows for unprecedented control and visibility. Operators can monitor entire production lines from a single dashboard, making informed decisions based on up-to-the-minute data.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Robots and autonomous systems serve as the muscle in modern chemical plants. They handle hazardous materials, perform repetitive tasks with tireless precision, and navigate complex environments.
Material handling robots can work around the clock, moving raw materials and finished products with minimal human intervention. Autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) zip through facilities, optimizing logistics and reducing the risk of accidents.
Advanced Process Control Systems (APCs)
APCs act as the control center for chemical processes. These sophisticated systems use complex algorithms to optimize reactions, improve yield, and maintain product quality.
Model Predictive Control (MPC) systems, for instance, use dynamic models to forecast process behavior and adjust parameters in real-time. Distributed Control Systems (DCSs) coordinate multiple processes across the plant, ensuring smooth operations from start to finish.
Automation and the Chemical Manufacturing Plant of the Future
As these technologies converge, they’re giving rise to a new paradigm in chemical manufacturing.
Digital Transformation
The automated chemical plant is, at its core, a digital entity. It integrates data from myriad sources to create a holistic view of operations.
Digital twins, virtual replicas of physical plants, allow operators to simulate and optimize processes before implementation. The integration of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) creates a seamless flow of information from the shop floor to the top floor.
Smart Factories and the Connected Plant
In the chemical plant of the future, every machine, sensor, and system is interconnected. This web of communication enables unprecedented levels of coordination and efficiency.
Operators can monitor plant operations in real-time, regardless of their physical location. When issues arise, remote troubleshooting and maintenance become possible, reducing downtime and improving safety.
Benefits of Automation in Chemical Manufacturing Plants
The shift towards automation brings a host of advantages to chemical manufacturers.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automated systems work tirelessly, streamlining workflows and optimizing resource utilization. Downtime is minimized as predictive maintenance identifies potential issues before they cause disruptions.
Enhanced Safety
By reducing the need for human presence in hazardous areas, automation significantly improves worker safety. Robots can handle dangerous chemicals and operate in extreme conditions without risk.
Improved Quality and Consistency
Automated systems maintain precise control over process parameters, ensuring consistent product quality. Real-time monitoring and data analysis allow for immediate corrective action when deviations occur.
Sustainability and Reduced Environmental Impact
Smart systems optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and control emissions. This not only benefits the environment but also improves the bottom line through resource efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Automated documentation and adherence to safety standards become easier with digital systems. Data-driven insights enable proactive risk assessment and management.
Cost Reduction and Increased Profitability
While the initial investment in automation can be substantial, the long-term benefits are clear. Lower labor costs, optimized production, and reduced raw material waste all contribute to improved profitability.
Challenges and Considerations for Automation Adoption in Chemical Manufacturing Plants
Despite its many benefits, the path to automation is not without obstacles.
High Initial Investment Costs
The upfront costs of automation can be daunting. Chemical companies must carefully plan their automation strategy and conduct thorough ROI analyses to justify the investment.
Technical Complexity and Integration Issues
Implementing advanced automation systems requires significant technical expertise. Companies must ensure they have access to skilled personnel and robust infrastructure to support these technologies.
Data Security and Cybersecurity Risks
As chemical plants become more connected, they also become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Comprehensive security measures are essential to protect sensitive data and critical systems.
Workforce Transition and Reskilling
Automation will inevitably change job roles within the chemical industry. Companies must invest in training programs and upskilling initiatives to help their workforce adapt to new technologies.
Regulatory and Standardization Considerations
The regulatory landscape for automated chemical plants is still evolving. Companies must stay abreast of emerging standards and best practices to ensure compliance.
The Road Ahead: Future Trends and Outlook for Automation in Chemical Manufacturing
As we look to the future, several trends are likely to shape the continued evolution of automation in chemical manufacturing.
Continued Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
We can expect to see even more sophisticated algorithms for process optimization and decision-making. These systems will become increasingly adept at handling complex, multi-variable processes.
Growth of Edge Computing and 5G
The rollout of 5G networks and advancements in edge computing will enable faster, more reliable real-time data processing. This will be crucial for time-sensitive applications in chemical manufacturing.
Greater Adoption of Robotics and Autonomous Systems
As robotics technology advances, we’ll see robots taking on increasingly complex tasks in chemical plants. This could include delicate assembly work or advanced analytical processes.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Automation will play a key role in driving sustainability in the chemical industry. From waste reduction to resource recovery, smart systems will help create more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
How to Prepare Your Chemical Plant for the Future of Automation:
- Assess Your Current State:
- Evaluate your existing infrastructure
- Identify areas ripe for automation
- Benchmark against industry leaders
- Develop a Roadmap:
- Define clear automation goals
- Create a phased implementation plan
- Align automation strategy with business objectives
- Invest in Technology:
- Research and select appropriate automation solutions
- Prioritize scalable, future-proof technologies
- Consider pilot projects to test new systems
- Train Your Workforce:
- Identify skills gaps in your organization
- Develop comprehensive training programs
- Foster a culture of continuous learning
- Embrace a Culture of Continuous Improvement:
- Encourage innovation at all levels
- Stay informed about emerging technologies
- Be prepared to adapt as the industry evolves
The automated chemical plant represents the future of the industry. By embracing these technologies and preparing for the challenges ahead, chemical manufacturers can position themselves at the forefront of this exciting transformation.
Ready to take the first step towards automating your chemical plant? Automation Ready Panels offers cutting-edge solutions tailored to the unique needs of the chemical industry. Our team of experts can help you navigate the complexities of automation, from initial assessment to full implementation. Don’t let your competitors leave you behind in the race to Industry 4.0. Contact Automation Ready Panels today and start your journey towards a smarter, safer, and more efficient chemical manufacturing future.
-
Large Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$24,073.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: Panelview 5000, ControlLogix 5580
$20,321.00 Select options -
Small Process Automation: ControlLogix 5580, UPS Battery Backup, Cellular Modem
$18,999.00 Select options -
Advanced Automation: Panelview 5000, Safety CompactLogix 5380
$10,269.00 Select options